Investigation of an evolutionary relationship between some snoRNAs and miRNAs
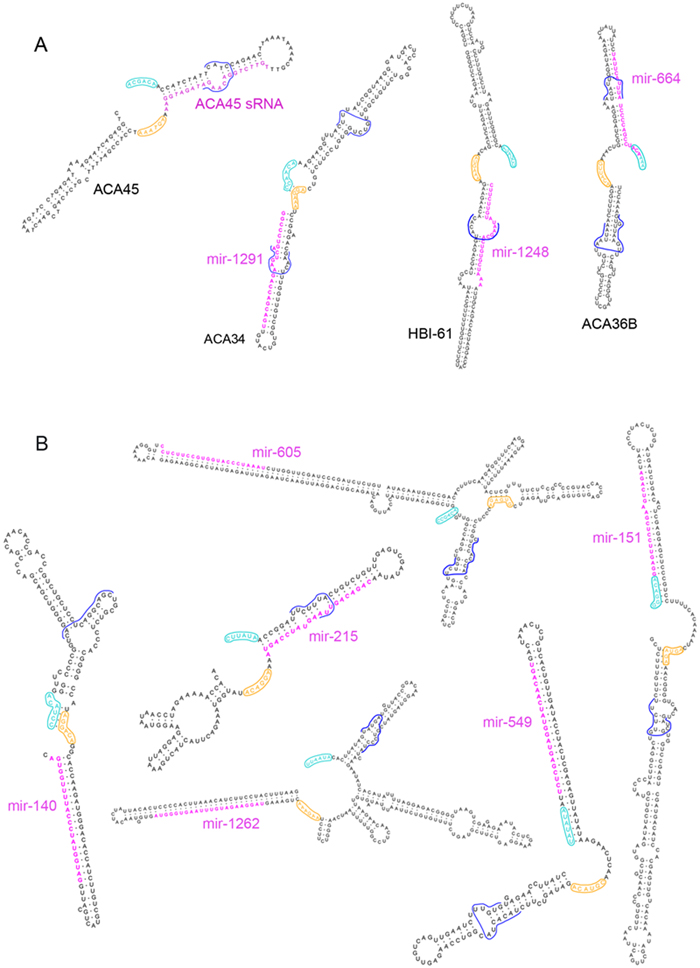
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are two classes of small non-coding regulatory RNAs, which have been much investigated in recent years. miRNAs are involved in the regulation of translation and snoRNAs participate in the post-transcriptional modification of rRNA. Recent sequencing projects have identified processed forms of snoRNAs that resemble miRNAs and a small number of snoRNAs have been shown to encode miRNAs in several organisms (Kawaji et al 2008, Ender et al. 2008, Saraiya and Wang 2008, and see panel A below).
We have systematically investigated a possible evolutionary relationship between snoRNAs and miRNAs using computational analyses. We identified twenty genomic regions encoding miRNAs with highly significant similarity to snoRNAs, both on the level of their surrounding genomic context as well as their predicted folded structure (see panel B below). We experimentally validated five of our predictions: the precursors of miR-151, miR-605, mir-664, miR-215 and miR-140 bind to dyskerin, a specific protein component of functional box H/ACA small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein complexes suggesting that these molecules have retained some H/ACA snoRNA functionality. (Scott et al. 2009).
References
- Ender C, Krek A, Friedlander MR, Beitzinger M, Weinmann L, et al. (2008) A Human snoRNA with MicroRNA-Like Functions. Mol Cell 32: 519-528.
- Kawaji H, Nakamura M, Takahashi Y, Sandelin A, Katayama S, et al. (2008) Hidden layers of human small RNAs. BMC Genomics 9: 157.
- Saraiya AA, Wang CC (2008) snoRNA, a Novel Precursor of microRNA in Giardia lamblia. PLoS Pathog 4: e1000224.
- Scott MS, Avolio F, Ono M, Lamond AI, Barton GJ (2009) Human miRNA precursors with box H/ACA snoRNA features. PLoS Comp Biol 5(9):e1000507.

