



Next: Method 2 -
Up: Allowing for Two
Previous: Allowing for Two
Segment A is chosen by cutting the chain at two points, x and y.
Therefore, B can consist of up to two segments, 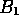 and
and
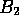 , depending on the positions of the boundaries.
The split value is calculated for all possible
segment A's formed by varying x and y. The
maximum split value is stored, together with the corresponding
values of x and
y, called
, depending on the positions of the boundaries.
The split value is calculated for all possible
segment A's formed by varying x and y. The
maximum split value is stored, together with the corresponding
values of x and
y, called 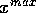 and
and 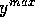 , which define
, which define 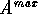 .
The maximum split value is compared with MSV and if
.
The maximum split value is compared with MSV and if 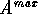 is not correlated with
is not correlated with 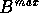 , then
, then 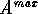 can be `extracted' from the `parent' domain to form a new
`child' domain (also referred to as a `subdomain'). The treatment
of
can be `extracted' from the `parent' domain to form a new
`child' domain (also referred to as a `subdomain'). The treatment
of 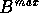 is the same for all three scans and is shown at the end
of method 3.
is the same for all three scans and is shown at the end
of method 3.
Note that the single segment scan would be able to deal with both the
situations that arise in Figure 1a and Figure 1b. However, it would not
be able to deal with the case shown in Figure 1c. To allow for this
eventuality a two segment scan is used.
as@bioch.ox.ac.uk
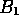 and
and
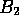 , depending on the positions of the boundaries.
The split value is calculated for all possible
segment A's formed by varying x and y. The
maximum split value is stored, together with the corresponding
values of x and
y, called
, depending on the positions of the boundaries.
The split value is calculated for all possible
segment A's formed by varying x and y. The
maximum split value is stored, together with the corresponding
values of x and
y, called 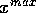 and
and 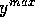 , which define
, which define 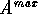 .
The maximum split value is compared with MSV and if
.
The maximum split value is compared with MSV and if 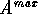 is not correlated with
is not correlated with 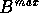 , then
, then 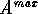 can be `extracted' from the `parent' domain to form a new
`child' domain (also referred to as a `subdomain'). The treatment
of
can be `extracted' from the `parent' domain to form a new
`child' domain (also referred to as a `subdomain'). The treatment
of 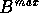 is the same for all three scans and is shown at the end
of method 3.
is the same for all three scans and is shown at the end
of method 3.



