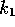 to
to 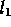 and
and 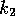 to
to 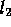 . The algorithm
scans this domain for subdomains in the following way.
. The algorithm
scans this domain for subdomains in the following way.




Now consider a domain made up of two segments, consisting of
residues 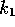 to
to 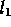 and
and 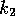 to
to 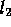 . The algorithm
scans this domain for subdomains in the following way.
. The algorithm
scans this domain for subdomains in the following way.
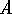 is made up of two
segments
is made up of two
segments 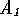 and
and 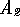 , formed by placing
four boundaries at
, formed by placing
four boundaries at 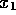 ,
, 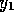 ,
, 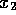 and
and 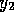 . Note that one of
the boundaries of both components of segment A must lie on the boundary of
the parent domain.
The split value between
. Note that one of
the boundaries of both components of segment A must lie on the boundary of
the parent domain.
The split value between 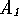 and
and 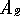 must show them to be
correlated when compared with MSV.
B can consist of up to two segments.
This split value is calculated for
all possible segment
must show them to be
correlated when compared with MSV.
B can consist of up to two segments.
This split value is calculated for
all possible segment 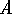 's formed by varying
's formed by varying
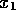 ,
, 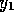 ,
, 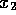 and
and 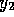 .
The maximum split value is stored,
together with the corresponding
values of
.
The maximum split value is stored,
together with the corresponding
values of 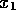 ,
, 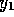 ,
, 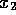 and
and 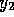 ,
called
,
called 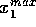 ,
, 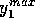 ,
,
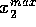 and
and 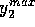 , which define
, which define 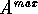 and
and 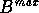 . The maximum split value is compared with MSV and if
. The maximum split value is compared with MSV and if 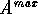 and
and 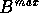 are not correlated, the parent domain is
split at this point.
are not correlated, the parent domain is
split at this point. 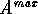 goes on to form a two segment
child domain.
goes on to form a two segment
child domain.
For all three scans, if 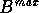 consists of only one segment,
it is considered to form a
single segment child domain. If
consists of only one segment,
it is considered to form a
single segment child domain. If 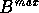 consists of two
segments, the split value between these two parts is calculated. If
the two segments are correlated, they are placed together to form a
single child domain made up of two segments, otherwise, they are
considered to be two separate, child domains. If
consists of two
segments, the split value between these two parts is calculated. If
the two segments are correlated, they are placed together to form a
single child domain made up of two segments, otherwise, they are
considered to be two separate, child domains. If 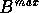 consists of three segments, the split values between all pairs are
calculated. If none of the pairs are correlated the segments are
considered to form three distinct child domains. If one of the pairs
are correlated, the two segments are placed together to form a two
segment child domain, the left over segment forming a single segment
child domain on its own. If two or three of the pairs are correlated,
the pair with the highest degree of correlation (i.e. lowest split
value) are placed together to form a two segment child domain, the
left over segment again forming a single segment child domain on its
own.
consists of three segments, the split values between all pairs are
calculated. If none of the pairs are correlated the segments are
considered to form three distinct child domains. If one of the pairs
are correlated, the two segments are placed together to form a two
segment child domain, the left over segment forming a single segment
child domain on its own. If two or three of the pairs are correlated,
the pair with the highest degree of correlation (i.e. lowest split
value) are placed together to form a two segment child domain, the
left over segment again forming a single segment child domain on its
own.



