NoD Virtual Appliance
The NoD virtual appliance is a way to run the NoD server locally without the need to connect to the internet. It is a complete and fully configured installation of the NoD server software on TurnKey Linux. To run the appliance you must first install one of the freely available VMWare Player or Oracle VirtualBox virtualisation systems. We have tested the NoD appliance with VMWare Player on Windows and Linux, and VirtualBox on Windows, Linux and Mac. On Windows and Linux we recommend VMWare Player since it requires less configuration. Mac users should use VirtualBox since the free VMWare player is not available on that platform. However, you are not limited to these virtualization systems and can use the NoD appliance with any other virtualization platform. Please note that currently, JPred secondary structure predictions are not available from the NoD virtual appliance. However, we are working on it.
How to install VMWare or VirtualBox
Please see the VMWare Player and Oracle VirtualBox websites for up to date instructions and downloads.
When to use the virtual appliance
The appliance suits users who would like to use the NoD web services locally, without an Internet connection, or want to keep their data private. The appliance is a self contained unit of software and as such may be used from any operating system. The appliance comes pre-configured to use 1 CPU and 512M of memory and the minimum amount of memory required is about 378M.
VMware Player appliance configuration
The free VMware Player can be used to run the NoD appliance from the Windows and Linux host operating systems, there is no support for Mac at the time of writing (December 2010). However, VMware Fusion, a commercial VMware product, offers virtual machine support for Mac computers too.
To run the NoD server on VMware player, unpack the NoD VM into one of the folders on your local hard drive. Open VMware Player, click "Open Virtual Machine" and point the Player to the location of the NoD VM, then choose the NoD.vmx file to open an appliance.
When you play the machine for the first time the Player might ask you whether "This virtual machine may have been moved or copied.", say that you have copied it. That is all.
VirtualBox appliance configuration
VirtualBox can be used to run NoD from Windows, Linux, Solaris or Mac host operating systems. Use the VitualBox "Import Appliance" option to import the NoD appliance. Please bear in mind that to benefit from multiple CPU support under the VirtualBox software you need to enable hardware virtualization extensions, such as Intel Virtualization VT-x or AMD-V support in the BIOS of your computer. Unfortunately, we were unable to find a reliable way to do it on Mac, so some Macs running VirtualBox will be limited to one CPU only, irrespective of the number of CPUs of the host machine. If you are in this situation you can buy the VMware Fusion to overcome these limitations.
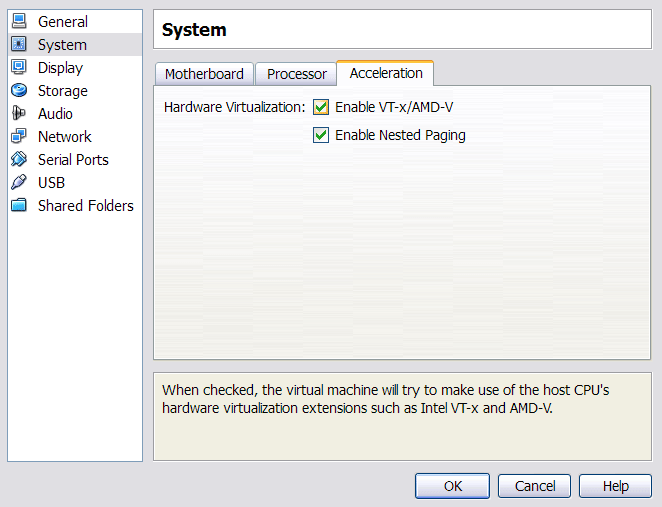
We found that, by default, virtualization extensions are enabled in VirtualBox irrespective of whether your computer supports them. You will get the VERR_VMX_MSR_LOCKED_OR_DISABLED exception if your computer does not support the extensions or their support is disabled. Just deselect the checkboxes shown on the screenshot below to solve the problem.
VirtualBox NoD VM configuration screenshot displaying virtualization settings.
NoD Appliance details
By default, the NoD virtual appliance is configured with 512M of memory and 1 CPU, but you are free to change these settings. If you have more than one CPU or CPU core on your computer you can make them available for the NoD virtual machine by editing virtual machine settings. Please bear in mind that more CPU power will not make a single calculation go faster, but it will enable the VM to do calculations in parallel. Similarly, you can add more memory to the virtual machine. More memory lets your VM deal with larger tasks.
The VMware Player screenshot below displays NoD VM CPU settings.
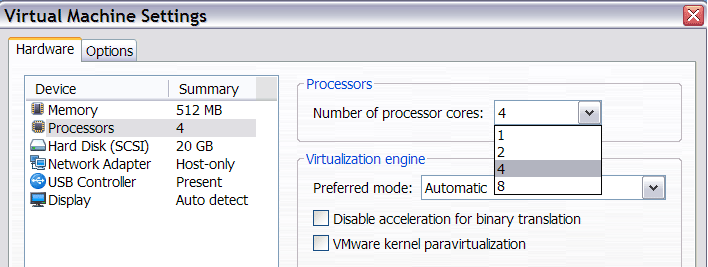
NoD appliance configuration:
VMware info
- Date of creation: 8 October 2010
- CPUs : 1
- RAM : 512 MB
- Networking : Host only (the VM has no access to the outside network, nothing from the outside network can access the VM)
- Hard disk : 20 GB (expanding)
- VMware tools : Installed
OS info
- OS : TurnKey Linux, based on Ubuntu 8.0.4 JEOS (Just-Enough-Operation-System)
- Installation : Oracle Java 6, Tomcat 6, MySQL 5.0, NoD v. 1.0
- Hostname : tomcat
- Patches : till date of creation
- IPv4 address : dhcp
- IPv6 address : auto
- DNS name : none
- Name server : dhcp
- Route : dhcp
- Keyboard : US_intl
Login credentials
- Root password: nod
Services
- Default virtual console Alt+F7
- Tomcat web server.
Access: http://VM_IP - NoD URL: http://VM_IP/nod
- Web Shell
Access: https://VM_IP:12320/ - Webmean
Access: https://VM_IP:12321/ - SSH/SFTP
Access: root@VM_IP
where VM_IP is the VM IP address. Under VMware Player host only networking, the first VM may have the IP address 192.168.227.128. Under VirtualBox host only networking, the first VM may have the IP address 192.168.56.101.
Accessing your NoD server VM
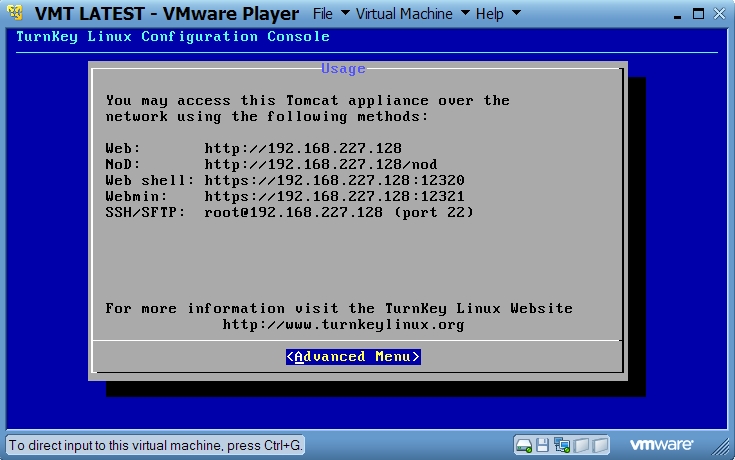
After booting the NoD VM, you should see a similar screen (as below), however, the IP address of your VM may be different. To access your NoD just type your VM IP address and NoD context name into your browser. This information is displayed after the VM has booted up.
The NoD address from the screenshot below is http://192.168.227.128/nod
Please wait for a few minutes after you see the configuration console before accessing the VM to let the server boot up completely.
If you click on Advanced Menu, you will see the configuration console, similar to the one below.
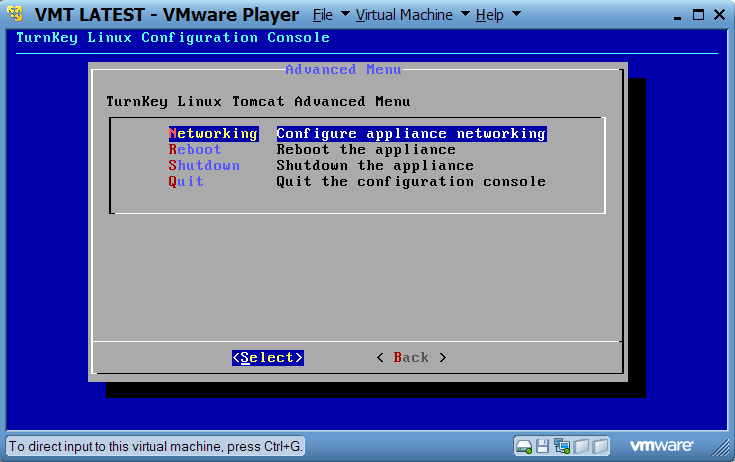
If you need to configure a static IP address the configuration console will help you with this. Shutting down the VM is best from the configuration console as well.
Using NoD on VM (Virtual Machine) Hints
VirtualBox VERR_VMX_MSR_LOCKED_OR_DISABLED exception
VERR_VMX_MSR_LOCKED_OR_DISABLED exception means that Intel Virtualization technology is disabled or not supported by your computer. If you have such a problem, please make sure you have configured the NoD VM with 1 CPU and disabled VT-X extensions. Alternatively you can enable virtualization extensions from the BIOS of your computer. Unfortunately, we cannot give you exact instructions on how to do this, as this would depend on your computer BIOS manufacturer. For MACs it may not be possible at all.
VMWare Player fails to open OVF file with "Failed to query source for information" error.
At the time of writing, the latest version of VMware Player 3.1.2 supported only a legacy OVF version 0.9, whereas OVF packaged with the NoD VM is version 1.0. Please use VMX - VMware specific configuration file with all VMware products.
Connecting to the Internet from NoD VM.
By default the NoD VM is configured to use host-only networking. This means that the host can communicate with the VM via a network, but no other machines can. Similarly, the VM cannot communicate with any other computers apart from the host. If you want to connect to the Internet from the VM, configure your VM to use a NAT network. However, you will not be able to connect to the VM from the host in such a case. If you want to be able to connect to your VM and let the VM connect to the internet at the same time you would have to use a Bridged network. In such a case you would have to configure the VM IP address manually (unless of course your network has a DHCP server to do that).
Contact details
If you have any problems or queries with this website, please send an email to

